As a responsible pet owner, you want to provide the best possible care for your furry friend. And part of that care involves understanding what foods and treats are appropriate for your dog’s age and development. One question many pet owners have is: “At what age can dogs have bones?”
While bones can provide numerous benefits for dogs, including dental health and mental stimulation, it’s important to wait until they are old enough to handle them safely. Giving bones to dogs too early can lead to serious health risks and complications.
- Key Takeaways
- At What Age Can Dogs Have Bones?
- Understanding Dog Bone Development
- Risks of Feeding Bones Too Early
- Guidelines for Introducing Bones to Dogs
- Choosing the Right Bones
- Monitoring and Supervising Bone Consumption
- Alternatives to Bones for Dental Health
- Common Bone-Related Issues in Dogs
- FAQ
- Q: At what age can dogs have bones?
- Q: What is the importance of understanding dog bone development?
- Q: Are bones safe for dogs?
- Q: What are the guidelines for introducing bones to dogs?
- Q: What types of bones are appropriate for dogs?
- Q: How should bone consumption be monitored and supervised?
- Q: What are the alternatives to bones for promoting dental health in dogs?
- Q: What are common bone-related issues in dogs?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Dogs can start having bones when their permanent teeth begin to come through, typically around 12 weeks old.
- Understanding your dog’s bone development is essential in determining when they can safely have bones.
- There are guidelines and recommendations for introducing bones to dogs that should be followed.
- Choosing the right types of bones and monitoring their consumption is crucial in ensuring your dog’s safety.
- There are alternative options for promoting dental health in dogs if bones are not suitable or preferred.
- Common bone-related issues in dogs should be considered before introducing bones into their diet.
At What Age Can Dogs Have Bones?
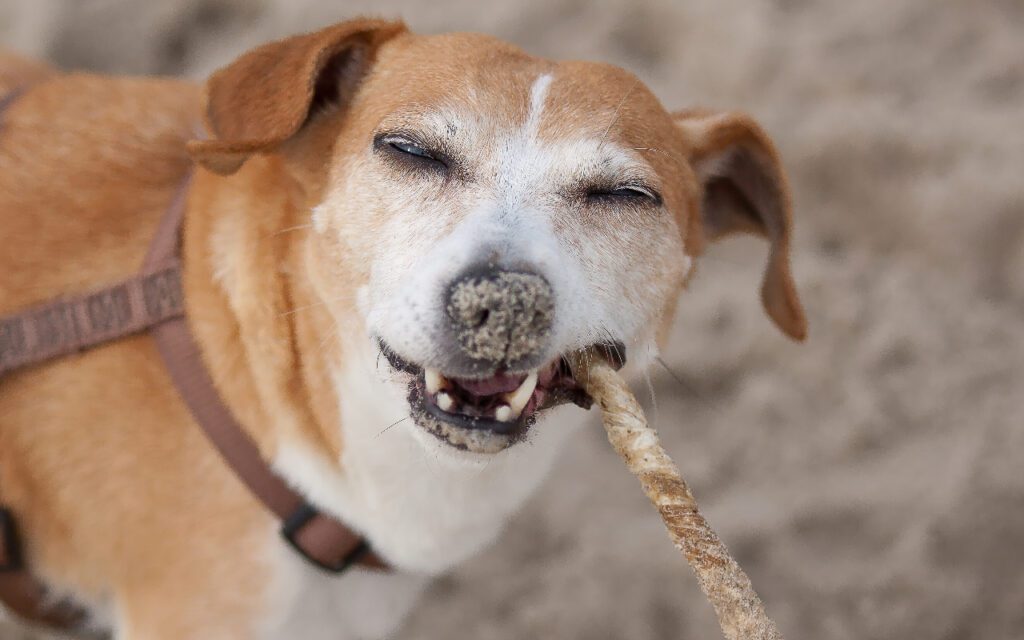

Dogs can start having bones at around 12 weeks old, which is typically when their permanent teeth begin to come through.
However, it’s crucial to ensure the bones are raw and not cooked, as cooked bones can splinter and pose a choking hazard or cause damage to your dog’s digestive tract.
The bones should be about the size of the dog’s head to prevent choking.
It’s also important to supervise your pet while they’re chewing on bones, especially puppies who are still learning what they can and can’t chew on.
Always consult with a vet if you have any concerns about introducing bones into your dog’s diet.
Risks of Feeding Bones Too Early

Feeding bones to puppies or dogs whose bones are still developing can result in several potential risks and dangers. While bones can provide numerous health benefits for dogs, it is essential to wait until they have reached an appropriate age before introducing them to their diet.
One of the main risks of feeding bones too early is the potential for fractured teeth. Puppies have softer teeth that are still developing, and chewing on hard bones can cause them to crack or break. This can lead to painful dental problems that require veterinary attention to correct.
Gastrointestinal blockages are another concern when feeding bones to dogs too early. Puppies and young dogs may not have the digestive system needed to break down and pass large bone fragments properly. This can result in blockages that prevent the dog from eating, cause vomiting and diarrhea, or require surgical intervention.
Choking hazards are also a potential risk when feeding bones to young dogs. Bones that are too small or have sharp edges can break off and become lodged in a dog’s throat. This can cause a life-threatening situation that requires immediate veterinary attention.
Overall, it is crucial to consider these risks carefully when deciding when to introduce bones to your dog’s diet. While bones can be beneficial, it is essential to wait until your dog’s bones have fully developed and to supervise them carefully while they consume them.
Guidelines for Introducing Bones to Dogs
Introducing bones to your dog’s diet can be a great way to promote dental health and provide them with a tasty treat, but it’s important to do so safely and at the appropriate age. Follow these guidelines when introducing bones to your furry friend:
| Factor to Consider | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Age | Wait until your dog is at least six months old before introducing bones, as their bones will have fully developed by this point. |
| Size and Breed | Select bones that are appropriate for your dog’s size and breed. Smaller dogs may require smaller bones, while larger dogs can handle larger ones without issue. |
| Health | Consider your dog’s overall health and any medical conditions they may have. Consult with a veterinarian before introducing bones if your dog has a history of digestive issues, dental problems, or other health concerns. |
| Supervision | Always supervise your dog while they are consuming bones to ensure their safety and minimize the risk of choking or other accidents. Remove any small bone fragments that could pose a hazard. |
Remember that every dog is different, and what works for one may not be optimal for another. Always monitor your dog’s behavior and health when introducing new foods or treats, and be prepared to make adjustments if necessary.
Choosing the Right Bones
When it comes to selecting bones for your furry friend, it’s crucial to choose ones that are safe and appropriate for their age, size, and breed. Here are some guidelines to keep in mind:
- Choose raw bones over cooked ones, as cooked bones can splinter and cause harm to your dog’s digestive system.
- Make sure the bone is the appropriate size for your dog. A bone that’s too small can be a choking hazard, while one that’s too big can cause damage to their teeth or jaws.
- Opt for larger, thicker bones that won’t break or splinter easily. These bones will also last longer, providing more entertainment and dental health benefits for your dog.
- Avoid bones from large game animals, such as deer or bison, as they can be tougher and more difficult for your dog to chew.
- If your dog has a history of digestive issues, it’s best to avoid bones altogether and seek alternative dental health options.
By carefully choosing the right bones for your dog and taking precautions to ensure their safety, you can provide them with a healthy and enjoyable chewing experience.
Monitoring and Supervising Bone Consumption
When introducing bones to dogs, it is crucial to monitor and supervise their consumption at all times. This is especially important during the initial stages of bone feeding, as dogs may not be familiar with the process and may become too enthusiastic, leading to accidents or injuries.
Ensure that the size and type of bone you choose is appropriate for your dog’s size, breed, and age. Additionally, make sure that the bone is not too hard or brittle, as it can splinter and cause harm to the dog’s mouth or digestive system.
It is recommended to offer bones only when you are present and available to supervise your dog’s behavior. This allows you to intervene if necessary and address potential issues before they escalate.
If your dog is showing signs of aggression or possessiveness towards the bone, it is best to remove it immediately to prevent any negative behavior from developing. Also, be sure to dispose of any leftover bones safely and keep them out of reach of other pets or children.
Alternatives to Bones for Dental Health
While bones are a popular option for promoting dental health in dogs, they may not be suitable or preferred for all pets. Fortunately, there are several alternative options that can help keep your dog’s teeth clean and healthy.
Dental chews: These treats are designed to provide a chewing experience that helps remove plaque and tartar buildup from your dog’s teeth. Look for chews that are specifically labeled as dental treats and check with your veterinarian to ensure they are appropriate for your dog.
Toy selection: Certain toys can also assist in removing plaque and tartar buildup. Look for toys that are specifically designed for dental health, such as those with ridges and bumps that can help clean your dog’s teeth as they chew and play.
Regular teeth brushing: Perhaps the most effective way to maintain your dog’s dental health is by regularly brushing their teeth. Using a dog-specific toothbrush and toothpaste, brush your dog’s teeth at least once a week. Talk to your veterinarian for advice on proper brushing techniques and to see if your dog may benefit from more frequent brushings.
Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best option for your pet’s dental health needs.
Common Bone-Related Issues in Dogs
Feeding bones to dogs can come with its fair share of complications and potential risks. It’s essential to be aware of the common bone-related issues that can arise in dogs.
One of the most prevalent issues is bone splintering, which can result in sharp fragments lodging in a dog’s throat, mouth, or digestive tract. Splintered bones can also cause severe internal injuries and infections, requiring surgery or even resulting in death.
Dental fractures are another common issue that can occur from bone consumption. Some bones may be too hard and cause significant damage, such as breaking a dog’s tooth or causing gum injuries. Over time, excessive bone chewing can also lead to worn-down teeth and damaged roots.
Furthermore, bones can also cause gastrointestinal problems in dogs. Consuming large pieces of bone can lead to stomach and intestinal blockages that can be life-threatening. Digestive issues like constipation and diarrhea are also common when dogs consume bones, causing discomfort and pain.
It’s crucial to be mindful of these potential issues and take measures to prevent them. Always supervise your dog when they are consuming bones and choose appropriate bones based on their size, breed, and chewing habits.
Note: If you notice any signs of distress or discomfort in your dog after consuming bones, it’s essential to seek veterinary attention immediately.
FAQ
Q: At what age can dogs have bones?
A: Dogs can have bones once their bones have fully developed, which is typically around 6 to 12 months of age, depending on the breed and size of the dog.
Q: What is the importance of understanding dog bone development?
A: Understanding dog bone development is crucial because feeding bones to dogs too early can lead to potential risks such as fractured teeth, gastrointestinal blockages, and choking hazards.
Q: Are bones safe for dogs?
A: While bones can be safe for adult dogs, feeding bones to puppies or dogs with developing bones can pose risks to their health and safety.
Q: What are the guidelines for introducing bones to dogs?
A: When introducing bones to dogs, it is important to consider factors such as the dog’s age, size, breed, and overall health. It is best to consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate time to start feeding bones.
Q: What types of bones are appropriate for dogs?
A: Dogs should be given bones that are safe, durable, and appropriate for their size and chewing habits. Avoid small, sharp, or cooked bones as they can pose a choking or splintering hazard.
Q: How should bone consumption be monitored and supervised?
A: It is essential to closely monitor and supervise dogs while they consume bones to ensure their safety. Never leave a dog unattended with a bone and be cautious of any signs of discomfort or difficulty while chewing.
Q: What are the alternatives to bones for promoting dental health in dogs?
A: If bones are not suitable or preferred, there are alternative options for promoting dental health in dogs, such as dental chews, toys specifically designed for dental care, and regular teeth brushing.
Q: What are common bone-related issues in dogs?
A: Bone-related issues in dogs can include bone splintering, dental fractures, and gastrointestinal problems. It is important to be aware of these potential complications and take necessary precautions.
Conclusion
Feeding bones to dogs can be a great way to promote dental health and provide a satisfying treat. However, it is important to understand the appropriate age at which dogs can have bones and the potential risks associated with feeding bones too early.
Waiting until a dog’s bones have fully developed is crucial to avoid issues such as fractured teeth, gastrointestinal blockages, and choking hazards. Additionally, selecting the right type of bone based on size, texture, and durability is important to ensure the safety of the dog.
It is also essential to monitor and supervise dogs while they consume bones to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries. If bones are not suitable or preferred, alternative options such as dental chews, toys, and regular teeth brushing can be effective in promoting dental health in dogs.




Leave a Reply