As a dog owner, it’s essential to understand the signs and potential causes of aggression in your furry friend.
Aggressive behavior in dogs can be dangerous and unpredictable, causing harm to both humans and other animals. Therefore, it’s crucial to recognize the early warning signs of aggression and take preventative measures.
In this article, we will explore the development of aggression in dogs and provide you with practical solutions for preventing and managing aggression in your furry friend.
- Key Takeaways:
- At What Age Do Dogs Get Aggressive?
- Understanding Dog Aggression Development
- Signs of Dog Aggression
- Aggression in Specific Dog Breeds
- Factors Influencing Dog Aggression
- Preventing Dog Aggression
- Managing Dog Aggression
- Training Techniques for Dog Aggression
- Aggression in Dogs Adulthood
- FAQ
- Q: At what age do dogs typically start exhibiting aggressive behavior?
- Q: What are the signs of dog aggression?
- Q: Are certain dog breeds more prone to aggression?
- Q: What factors can influence dog aggression?
- Q: How can dog aggression be prevented?
- Q: How can dog aggression be effectively managed?
- Q: What training techniques can be used for dog aggression?
- Q: Can dogs exhibit aggression in adulthood?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
- Aggressive behavior in dogs can be dangerous and unpredictable, causing harm to both humans and other animals.
- There is no easy answer to the question, “At what age do dogs get aggressive?” as different dogs can exhibit aggression at any age.
- Recognizing key factors that can cause aggressive behavior in dogs is essential in preventing or managing aggression in your dog.
At What Age Do Dogs Get Aggressive?

Dogs can start to show signs of aggression when they reach puberty, typically between six to nine months of age.
Aggressive behavior in dogs can start to appear at various stages of their life, depending largely on individual factors and circumstances.
Some dogs may begin to show signs of aggression as young as two weeks old, even before their eyes have opened.
However, more commonly, noticeable signs of aggression may start to emerge around the time a dog reaches puberty, which is typically between six and nine months of age.
Inter-dog aggression, in particular, is often associated with this period of sexual maturity. It’s important to note that aggression is not a behavior that naturally increases as dogs age.
Instead, it can be influenced by factors such as lack of socialization, improper training, and certain genetic and hereditary factors.
Understanding Dog Aggression Development
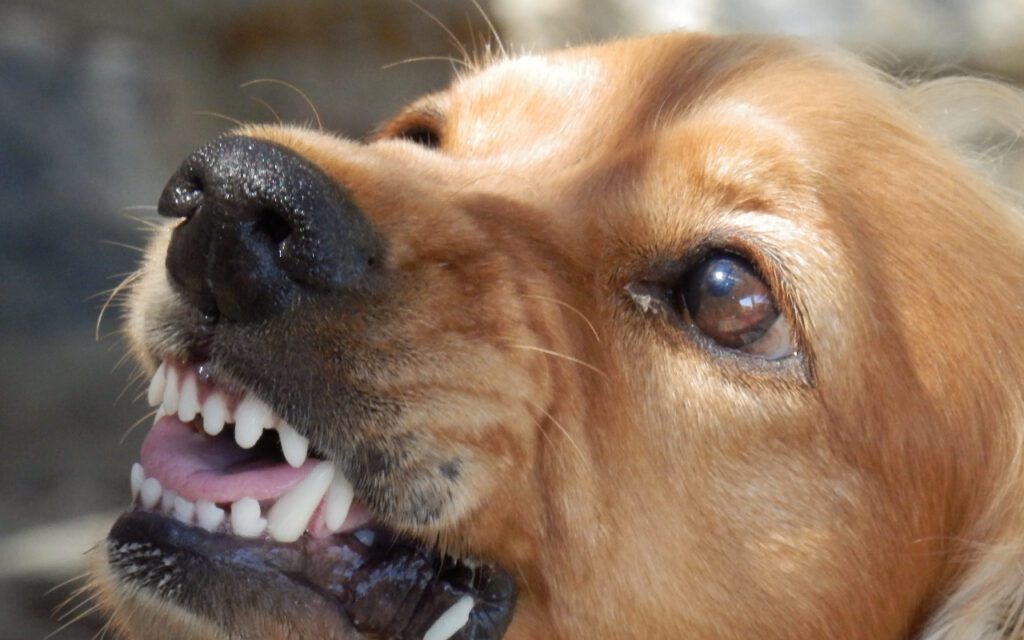

Dog aggression is a complex behavior that can develop in various stages of a dog’s life. Puppies, for instance, can display aggressive tendencies as early as eight weeks old. Understanding how dog aggression develops can help pet owners prevent and manage this issue before it becomes a serious problem.
Aggression in puppies:
Puppies can exhibit various signs of aggression which are normal during their development stages. For instance, growling, snapping, and biting during play is normal puppy behavior and should not be confused with aggression.
However, puppies can also develop aggressive tendencies due to negative interactions with humans or other dogs. Such interactions could include rough handling, teasing, or being attacked by other dogs.
Aggression in adult dogs:
Aggression can develop in a dog’s adulthood due to various factors, including lack of socialization, poor training, or other negative experiences. Unlike puppies, adult dogs’ aggressive behavior can cause serious harm to other dogs and humans. Therefore, it is crucial to address and manage this issue quickly and effectively.
Factors Contributing to Dog Aggression
Several factors can contribute to dog aggression in puppies and adult dogs. These include:
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Socialization | Puppies require early socialization to develop appropriate behaviors towards other dogs and humans. Lack of socialization can result in fear, anxiety, and aggression towards unfamiliar people and pets. |
| Training | Inadequate or inappropriate training can result in dogs that are difficult to control and prone to aggressive behavior. Positive reinforcement training can help develop desirable behaviors while minimizing aggression. |
| Environment | Some dogs become territorial and aggressive towards unfamiliar visitors to their home or yard. Dogs that lack proper exercise and mental stimulation can also become aggressive due to boredom and frustration. |
| Past experiences | Dogs that have been abused or had negative interactions with humans or other animals may develop aggressive tendencies as a response to these experiences. |
The above factors can interplay with each other, causing a complex set of aggressive behaviors. An effective approach to managing aggression should involve addressing each of these factors.
Signs of Dog Aggression
Dog aggression can manifest in many different ways. It is important for dog owners to recognize the signs of aggression in order to prevent dangerous situations from occurring. Some common signs of dog aggression include:
- Growling or snarling
- Baring teeth or showing other threatening body language
- Barking aggressively
- Lunging or charging at people or other animals
- Biting or nipping
- Refusal to back down or retreat from a situation
- Guarding food or toys aggressively
It is important to note that not all aggressive behavior in dogs is overtly threatening. Subtle signs of aggression can also be present and should not be ignored. These may include:
- Stiff body posture
- Tensed muscles
- Lip licking or yawning when not tired
- Avoiding eye contact
- Pinned back ears
- Tail held high or straight up
If you notice any of these signs in your dog, it is important to consult with a professional and take appropriate measures to prevent aggressive behavior.
Aggression in Specific Dog Breeds
Dog breeds vary widely in terms of their predisposition towards aggression. While no breed is inherently aggressive, certain breeds may be more prone to aggressive behavior due to genetics and breed characteristics.
One example of a breed that has been associated with aggression is the Pit Bull. These dogs were originally bred for dog fighting, which may have contributed to their aggressive tendencies. However, with proper socialization, training, and responsible ownership, Pit Bulls can make loving and loyal pets.
Other breeds that have been linked to aggression include Rottweilers, Doberman Pinschers, and German Shepherds. These breeds were originally bred for protection and guarding, which may have contributed to their tendency towards territorial behavior and aggression towards strangers.
It’s important to note that aggression is not limited to these breeds alone. Any dog, regardless of breed, age, or size, can exhibit aggressive behavior under certain circumstances.
Aggression in Specific Dog Breeds: The Role of Breed Characteristics
When it comes to aggression in specific dog breeds, it’s important to consider the role of breed characteristics. For example, some breeds are known for their high energy levels and require plenty of exercise and mental stimulation to prevent boredom and frustration, which can lead to aggressive behavior.
Other breeds may have a high prey drive, which can lead to chasing and potentially aggressive behavior towards small animals or children. Understanding the unique characteristics of your dog’s breed can help you anticipate potential triggers for aggression and take proactive measures to prevent it.
Factors Influencing Dog Aggression
Dog aggression is influenced by various factors that shape a dog’s behavior. It is important to identify these factors to prevent and manage aggressive tendencies in dogs.
Socialization
Socialization plays a crucial role in shaping a dog’s behavior. Dogs that are not properly socialized may become fearful and aggressive towards unfamiliar people, animals, and environments. Early socialization, between the ages of 3-14 weeks, can help ensure that dogs are comfortable and confident in different environments and situations.
Environment
A dog’s environment can significantly impact its behavior. Dogs that are kept in stressful or isolated environments may become fearful or aggressive. Providing a safe, comfortable, and stimulating environment that meets a dog’s physical and mental needs can help prevent aggression.
Training
Training is an essential aspect of preventing and managing dog aggression. Positive reinforcement training methods can help build a strong bond between a dog and its owner, while also reinforcing good behavior.
Consistent training routines that focus on reinforcing desired behaviors can reduce aggressive tendencies and teach dogs appropriate ways to interact with people and other animals.
Past Experiences
Past experiences, such as abuse or neglect, can significantly impact a dog’s behavior. Dogs that have experienced trauma may exhibit fear and aggression as a result. It is important to provide these dogs with patience, understanding, and consistent training to help them overcome their past experiences and prevent future aggressive behavior.
Breed Characteristics and Genetics
Some dog breeds are more predisposed to aggression than others. Breed characteristics, genetics, and breeding history can all influence a dog’s behavior. Owners of breeds that are known for aggression should take extra care to socialize and train their dogs, and seek professional help if necessary.
Preventing Dog Aggression
Preventing dog aggression is crucial for the safety of both the dog and their surroundings. There are several effective prevention methods that can help avoid the development of aggressive behavior:
- Early socialization: Introducing your dog to people, other animals, and various environments at an early age can help them become comfortable and well-adjusted.
- Positive reinforcement training: Rewarding good behavior with treats or praise can encourage your dog to repeat that behavior. Punishing your dog for bad behavior can have negative consequences and should be avoided.
- Creating a safe environment: Providing a safe and secure environment for your dog can help avoid situations that can trigger aggressive behavior. Ensuring your dog has a comfortable space to rest, eat, and play, and avoiding stressful environments can help prevent aggression.
However, if your dog is already exhibiting aggressive behavior, it is important to seek professional help to manage and address the issue.
Managing Dog Aggression
Managing dog aggression can be a challenging task, but with the right strategies, it is possible to reduce and control aggressive behavior in dogs. Here are some effective techniques for managing dog aggression:
Behavior Modification
One of the most common approaches to managing dog aggression is behavior modification. This technique involves identifying the triggers that cause aggressive behavior in dogs and gradually changing their response to those triggers.
Behavior modification often involves a combination of positive reinforcement training, desensitization, and counterconditioning. It is essential to work with a professional trainer or behaviorist when using behavior modification, as they can provide guidance and support throughout the process.
Setting Boundaries
Setting clear boundaries and rules for your dog is an important step in managing aggression. Dogs need to understand what is expected of them and what behaviors are not acceptable. Consistency is key when setting boundaries, and it is important to enforce rules consistently to avoid confusion for your dog.
Providing Mental and Physical Stimulation
Dogs who are bored or lack mental and physical stimulation are more likely to exhibit aggressive behaviors. Providing ample opportunities for exercise, play, and mental stimulation can help to reduce aggression in dogs.
Interactive toys, puzzles, and games can keep dogs entertained and engaged, while regular walks and playtime can ensure they get enough exercise and social interaction.
Implementing Consistent Training Routines
Consistent training routines can help to establish and reinforce good behavior in dogs. Positive reinforcement training techniques, such as clicker training, can help to encourage good behavior while discouraging bad behavior. It is important to be patient and consistent when training dogs, as results may take time to see.
Managing dog aggression can be a long process, and it is important to seek professional help when needed. With patience, persistence, and the right techniques, it is possible to reduce and control aggressive behavior in dogs.
Training Techniques for Dog Aggression
When it comes to dealing with dog aggression, training is an essential tool for both prevention and management. Below are some effective training techniques that can help address aggressive behavior in dogs:
Positive Reinforcement Training
Positive reinforcement training involves rewarding your dog for good behavior instead of punishing them for bad behavior. When dealing with aggression in dogs, this technique involves rewarding them for calm and non-aggressive behavior, such as sitting or lying down. This method helps encourage good behavior and can effectively retrain aggressive tendencies.
Desensitization and Counterconditioning
This technique aims to change a dog’s emotional response to a particular trigger that causes aggression. It involves gradually exposing the dog to the trigger while ensuring they remain calm and relaxed.
Over time, the dog’s association with the trigger changes, resulting in a more positive emotional response. This method requires patience, consistency, and a good understanding of a dog’s behavior.
Working with a Professional Trainer
Aggression in dogs can be challenging to manage, and it is essential to seek professional help when needed. A professional trainer can assess the dog’s behavior and create a customized training plan that addresses specific triggers and behaviors.
In addition, trainers can provide guidance and support throughout the training process, helping to ensure success.
Overall, training is a crucial aspect of addressing dog aggression. Positive reinforcement, desensitization and counterconditioning, and working with a professional trainer are all effective techniques that can help manage aggressive tendencies in dogs.
Aggression in Dogs Adulthood
While aggression in puppies is not uncommon, it’s important to note that aggression can manifest in dogs at any age. Even if your dog has never exhibited aggressive behavior before, it’s essential to remain vigilant and take steps to prevent and manage aggression as they age.
One of the most important things you can do to prevent aggression in adult dogs is to maintain consistent training throughout their lives. This includes ongoing socialization, positive reinforcement, and setting clear boundaries.
If your adult dog does begin to exhibit signs of aggression, it’s important to seek professional help as soon as possible. A trained and experienced dog behaviorist can help you identify the root causes of your dog’s aggression and work with you to develop a personalized behavior modification plan.
Management techniques such as creating a safe and secure environment, providing mental and physical stimulation, and consistent training routines can also play a critical role in managing aggression in adult dogs.
By proactively addressing aggressive behavior and seeking professional help when necessary, you can help ensure that your dog remains happy, healthy, and safe throughout their life.
FAQ
Q: At what age do dogs typically start exhibiting aggressive behavior?
A: Dogs can start exhibiting aggressive behavior at any age, but it is most commonly seen during adolescence, between 6 months and 2 years old.
Q: What are the signs of dog aggression?
A: Signs of dog aggression can include growling, snarling, snapping, lunging, and biting. Other subtle signs may include stiff body language, raised hackles, and intense staring.
Q: Are certain dog breeds more prone to aggression?
A: Certain dog breeds may have a predisposition towards aggression due to genetics and breed characteristics. However, it is important to remember that individual temperament can vary within a breed.
Q: What factors can influence dog aggression?
A: Dog aggression can be influenced by factors such as socialization, environment, training, and past experiences. These factors play a role in shaping a dog’s behavior and should be considered when addressing aggression.
Q: How can dog aggression be prevented?
A: Dog aggression can be prevented through early socialization, positive reinforcement training, creating a safe environment, and seeking professional help when needed. These methods can help promote good behavior and prevent aggression from developing.
Q: How can dog aggression be effectively managed?
A: Dog aggression can be effectively managed through behavior modification techniques, setting boundaries, providing mental and physical stimulation, and implementing consistent training routines. These strategies can help control and reduce aggressive behavior.
Q: What training techniques can be used for dog aggression?
A: Training techniques such as positive reinforcement, desensitization and counterconditioning, and working with a professional trainer can be effective in addressing dog aggression. These methods focus on rewarding desired behavior and teaching dogs appropriate ways to interact.
Q: Can dogs exhibit aggression in adulthood?
A: Yes, dogs can exhibit aggression in adulthood. It is important to continue training and managing a dog’s behavior throughout their life to prevent and address aggression. Consistency and positive reinforcement are key.
Conclusion
Understanding and preventing dog aggression is crucial for both the safety of the dog and those around them. Aggressive behavior in dogs can develop at any age, but early recognition and intervention can prevent it from worsening.
Factors such as genetics, socialization, environment, and past experiences can all contribute to a dog’s tendency toward aggression. Proper training, positive reinforcement techniques, and consistent management are essential in preventing and managing aggression in dogs.
If you are experiencing aggression issues with your dog, seeking professional help from a certified dog trainer or animal behaviorist can be beneficial in addressing the problem.




Leave a Reply