Dogs are susceptible to a variety of health problems, and one common issue that pet owners may notice is swelling under their dog’s tail.
While it can be alarming to see, there are a variety of causes for the swelling, and treatment options depend on the underlying cause.
In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for swelling under a dog’s tail. We will also provide tips on how to prevent this from happening in the first place!
Swelling under a dog’s tail could be due to an impacted anal gland caused by factors such as diarrhea and constipation, a cyst that could be infected, or a tumor called adenocarcinoma that may require treatment.
What Causes Swelling Under My Dog’s Tail?
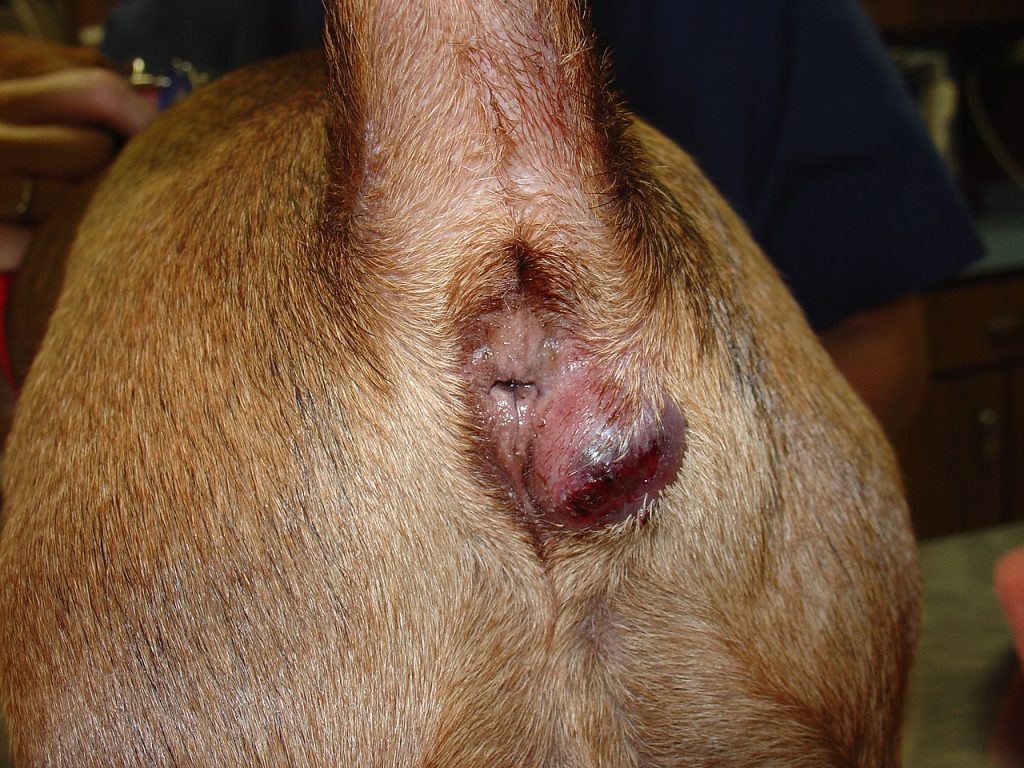
Swelling under a dog’s tail can be due to various reasons including impacted anal sacs, abscesses, tumors, infections, or conditions like Limber Tail Syndrome.
Impacted Anal Sacs
Impacted anal sacs are a common cause of swelling under a dog’s tail. Dogs have two small pouches on either side of their anus which secrete a distinct scent that they use to mark territory.
Sometimes, these sacs can become blocked, leading to discomfort and swelling. Regular grooming and a high-fiber diet can help prevent this issue says AKC.
Abscesses and Infections
Abscesses are pockets of pus that can form when the body reacts to an infection or injury. If your dog has an abscess or infection in the anal area, it could cause swelling and discomfort.
Proper hygiene and regular checks can help detect and treat these issues early.
Tumors
Benign or malignant tumors can also cause swelling under a dog’s tail. While tumors are less common, they can be serious and require immediate veterinary attention.
Regular vet check-ups can help in early detection and treatment of such conditions as per PetMD.
Limber Tail Syndrome
Limber Tail Syndrome is a condition that affects mainly working breeds and causes pain and swelling at the base of the tail. It’s often caused by overuse of the tail or exposure to cold water.
Providing adequate rest and avoiding sudden exposure to cold can help prevent this syndrome.
Symptoms of Anal Sack Problems in Dogs
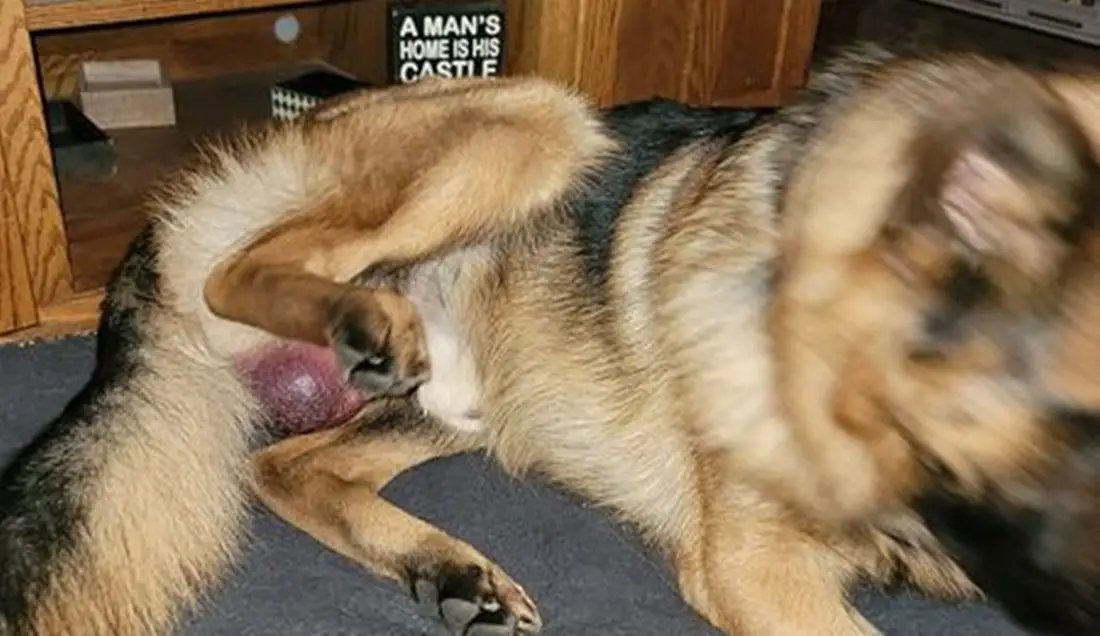
Symptoms of anal sack problems in dogs can range from scooting and excessive licking of the area to visible redness, swelling, and discharge.
Scooting and Discomfort
One of the first signs of anal sack issues in dogs is often scooting, which involves the dog dragging its rear end across the floor.
This behavior is typically a response to discomfort or itchiness. The dog may also show signs of general discomfort, such as whimpering or becoming withdrawn.
In my years as a vet, I’ve seen many dogs presenting with this symptom, and it’s usually a clear indication that the anal sacks need to be examined.
Excessive Licking or Biting
Dogs with anal sack problems may also excessively lick or bite at the affected area. This is another attempt to alleviate discomfort or itchiness. However, constant licking or biting can lead to further irritation and potential infection, so it’s important to seek veterinary care if you notice this behavior.
Redness, Swelling, and Discharge
Visible symptoms such as redness, swelling, or discharge around the anal area are clear indicators of anal sack problems.
These symptoms suggest that an infection or abscess may have developed. In more severe cases, the sacs may rupture, releasing a greenish-yellow or bloody pus.
Remembering a case from my practice, a German Shepherd came in with a ruptured anal sac. Immediate treatment was necessary to clean the area and start the dog on antibiotics to fight the infection.
Changes in Bowel Movements
Anal sack problems can make defecation painful for dogs. They may strain during bowel movements or show signs of pain. In some cases, they might even avoid eating or drinking to prevent having to defecate.
How To Treat Swelling Under Dog’s Tail
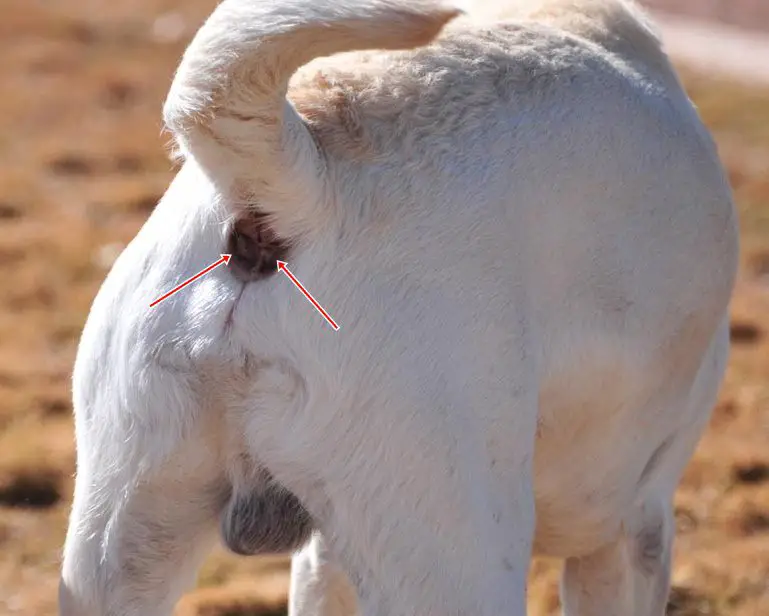
The treatment for swelling under the dog’s tail will depend on what is causing it. The most common causes of swelling under a dog’s tail are impacted anal glands, a cyst, or a tumor.
Here is how to treat swelling under the dog’s tail accordingly:
If the swelling under the dog’s tail is caused by impacted anal glands
Impacted anal glands are a common problem in dogs. The anal glands are two small sacs located on either side of the anus. They are connected to the rectum by a duct, and their function is to release a foul-smelling liquid when the dog defecates.
This liquid helps to mark the dog’s territory and also contains pheromones that help the dog communicate with other dogs.
If the anal glands become impacted, it means that the ducts are blocked and the glands cannot release their contents.
This can be very painful for the dog and may lead to infection if not treated promptly. Treatment involves expressing the glands manually or surgically removing them. In some cases, antibiotics may also be necessary.
If the swelling under the dog’s tail is caused by a cyst
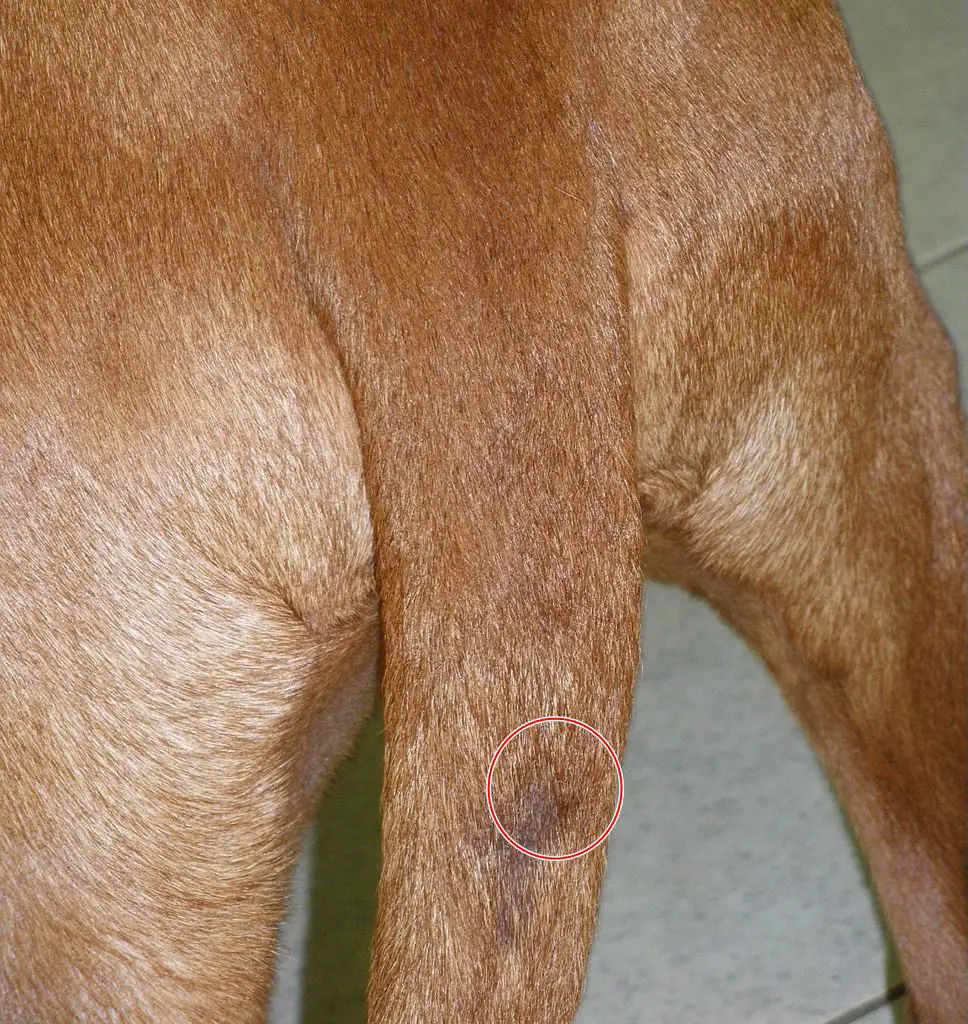
There are a few options for treating anal cysts in dogs. The most common is to lance and drain the cyst, which can be done at home or by your veterinarian.
First, clean the area around the cyst with a bar of mild soap and warm water. Then, apply an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment to the area. Finally, keep an eye on the cyst and monitor it for any changes.
If the cyst appears to be getting larger or if it is causing your dog discomfort, contact your veterinarian.
They may recommend special shampoos or ointments to help treat the cyst or they may need to drain it. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the cyst.
Treating swelling under the dog’s tail caused by abscesses and infections
Treating swelling under a dog’s tail caused by abscesses and infections involves a combination of professional veterinary care, medication, and at-home monitoring.
If your dog has a swollen area under its tail due to an abscess or infection, the first step is to seek immediate veterinary care.
The vet will likely perform a physical examination and may need to do further tests to determine the cause of the swelling.
Treatment typically involves cleaning the area, draining the abscess if present, and prescribing antibiotics to treat the infection.
If the swelling under the dog’s tail is caused by a tumor
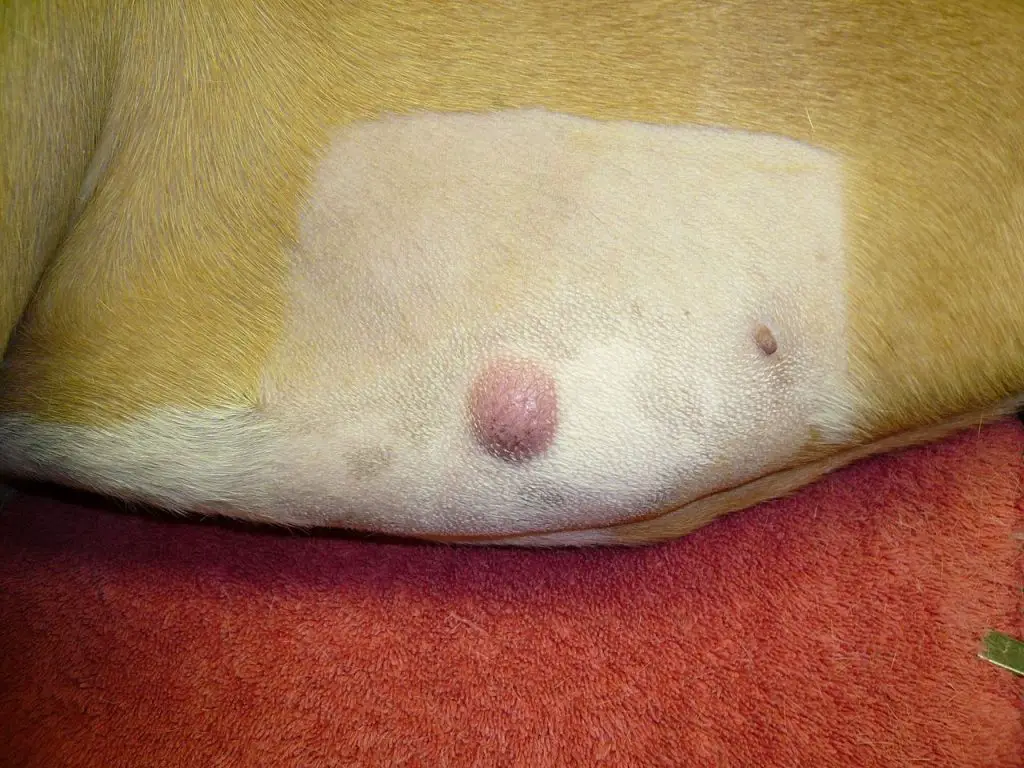
Tumors in dogs’ anal areas are not typically life-threatening, but they can be quite painful. If your dog has a tumor in this area, it is important to have it checked out by a veterinarian as soon as possible.
There are a few different options for treating tumors in dogs, depending on the type and location of the tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, surgery may be recommended to remove it. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may also be used to treat the tumor.
If the tumor is benign, your veterinarian may recommend a course of treatment that includes observation, medication, or both.
Treatment will vary depending on the type of tumor and your dog’s overall health. Your veterinarian will develop a treatment plan that is best for your dog based on all of these factors.
Treating limber tail syndrome
Treating limber tail syndrome, which causes swelling under a dog’s tail, typically involves rest, pain management, and careful monitoring of the dog’s recovery.
Limber tail syndrome, also known as acute caudal myopathy, is a condition often seen in dogs with long tails that leads to pain and swelling at the base of the tail.
The mainstay of treatment for this condition is providing your dog with ample rest, administering prescribed pain management medications, and monitoring their recovery closely.
How To Prevent Swelling Under Dog’s Tail
Preventing swelling under a dog’s tail primarily involves regular checks for anal gland issues, maintaining a high-fiber diet, and ensuring routine vet check-ups.
Regular Checks for Anal Gland Issues
One of the key ways to prevent swelling under a dog’s tail is to regularly check for any signs of anal gland issues. These can include discomfort when sitting, scooting their rear on the ground, licking or biting at the anal area, and a foul smell coming from the anus.
If these symptoms are noticed, it’s important to seek veterinary advice immediately to prevent the condition from escalating.
Maintain a High-Fiber Diet
A high-fiber diet can help keep your dog’s anal glands healthy by promoting regular bowel movements, which can naturally express the glands. This can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes high-quality commercial dog food, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Routine Vet Check-ups
Regular visits to the vet for routine check-ups can help in early detection and treatment of potential anal gland issues. The veterinarian can manually express the anal glands if necessary and provide advice on how to maintain the health of your dog’s anal glands.
Exercise and Hydration
Regular exercise and hydration are important in preventing anal gland issues. Regular walks and playtime can help stimulate bowel movements, while adequate hydration can prevent constipation, both of which can help in naturally expressing the anal glands.
When To Seek Veterinary Assistance For Swelling Under Dog’s Tail

Seeking veterinary assistance for swelling under a dog’s tail should be immediate when you notice physical changes, discomfort, or unusual behavior in your pet that could indicate an underlying issue.
When it comes to swelling under a dog’s tail, it’s crucial to seek veterinary assistance as soon as possible.
Physical changes such as visible lumps, redness, discharge, or noticeable swelling are clear signs that something is amiss. These symptoms could indicate a range of issues, from anal gland complications to infections, abscesses, or even tumors.
From my experience working as a vet, I can’t stress enough the importance of promptly addressing these symptoms.
I recall treating a Labrador Retriever that had been showing signs of discomfort and had a visible swelling under its tail.
After examination, we discovered an infected anal gland that required immediate treatment. We managed to drain the gland and prescribed antibiotics, which led to a full recovery.
In addition to physical changes, dogs may also exhibit behavioral changes that signal discomfort or pain in the area. T
his can include scooting, excessive licking or biting at the area, changes in bowel movements, or general signs of discomfort. If you notice any of these behaviors, it’s best to consult with a vet without delay.
What You Can Do At Home For Swelling Under Dog’s Tail
There are several at-home remedies you can use for swelling under your dog’s tail, including warm compresses, keeping the area clean, diet changes, and over-the-counter treatments.
Warm Compresses
Warm compresses can help reduce inflammation and soothe discomfort associated with anal gland issues. To do this, dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water, soak a clean cloth in the solution, and apply it to the affected area.
This can be done a few times a day to alleviate discomfort. As a vet, I’ve recommended this simple yet effective remedy to many pet owners to provide temporary relief.
Keeping the Area Clean
Keeping the area clean is crucial to prevent infection and further complications.
If your vet has cleaned your dog’s bottom, you should continue this at home using warm salty water and cotton wool pads. This helps to keep the area clean and reduce irritation.
Diet Changes
Diet can play a significant role in preventing and managing anal gland issues in dogs.
Increasing fiber intake can help firm up stools, which in turn can assist in naturally expressing the anal glands during defecation.
It’s important to consult with your vet before making significant changes to your pet’s diet.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Over-the-counter treatments like hygienic wipes or medicated sprays can also be beneficial. These products can help keep the area clean and provide some relief from discomfort.
In some cases, a plain Neosporin might be used to soothe the area, but it’s essential to ensure your dog doesn’t lick it.
FAQs
Q: How can I tell if my dog has swelling under its tail?
A: You may notice your dog licking or biting the area excessively, and you might also feel a lump or notice swelling under the tail when you examine your dog.
Q: Can anal gland problems cause swelling under a dog’s tail?
A: Yes, anal gland problems such as impaction or infection can lead to swelling under a dog’s tail. If the anal glands become blocked, fluid build-up can occur, causing discomfort and swelling.
Q: What should I do if I notice swelling under my dog’s tail?
A: It is important to have your dog examined by a veterinarian if you notice swelling under its tail. The veterinarian will be able to determine the underlying cause and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Q: Can allergies cause swelling under a dog’s tail?
A: Yes, allergies can cause inflammation and swelling under a dog’s tail. Allergic reactions to certain foods, environmental factors, or parasites can lead to localized swelling in this area.
Q: Are there any home remedies to treat swelling under a dog’s tail?
A: It is best to consult with a veterinarian before attempting any home remedies for swelling under a dog’s tail. The appropriate treatment will depend on the underlying cause, and self-treatment may not address the root issue.
Q: Is swelling under a dog’s tail a sign of cancer?
A: While swelling under a dog’s tail can sometimes be caused by tumors or cancer, it is important not to jump to conclusions. Many other non-cancerous conditions can also cause swelling in this area. A veterinarian can perform diagnostic tests to determine the cause of the swelling.
Q: Can trauma or injury cause swelling under a dog’s tail?
A: Yes, trauma or injury to the tail area can cause swelling. It is possible for a dog to injure its tail by wagging it too vigorously, getting it caught in something, or being involved in an accident. If you suspect your dog has been injured, it is important to seek veterinary care.
Q: How are anal sac problems treated?
A: Treatment for anal sac problems may include expressing the impacted glands, administering antibiotics if there is an infection, or in some cases, surgical removal of the glands. Your veterinarian will recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the severity of the condition.
Q: Can I prevent swelling under my dog’s tail?
A: While some causes of swelling under a dog’s tail may not be preventable, there are a few things you can do to minimize the risk. Regularly expressing the anal glands, maintaining proper hygiene in the tail area, and addressing any underlying allergies or potential irritants can help reduce the likelihood of swelling in this area.
Conclusion and final thoughts
In conclusion, while swelling under a dog’s tail can be concerning for pet owners, it is important to remember that there are many potential causes for this issue and not all of them are serious or life-threatening.
It is always best to consult with a veterinarian if you notice any abnormal swelling in your dog’s tail area.
By accurately monitoring and addressing the issue, we can ensure our furry friends receive the proper care and treatment they need to stay happy and healthy.